In an era defined by rapid technological advancements, global interconnectedness, and ever-evolving consumer demands, the landscape of global supply chain finance is undergoing a transformation of unprecedented magnitude. As businesses adapt to the demands of an increasingly complex marketplace, the traditional paradigms of supply chain financing are being redefined.
The symbiotic relationship between finance and supply chain management has always been the linchpin of operational success for businesses worldwide. However, with the advent of cutting-edge technologies like blockchain, artificial intelligence, and IoT, coupled with a heightened focus on sustainability and social responsibility, the dynamics of supply chain finance are poised to undergo a seismic shift.
New trends, technologies, and strategies are constantly emerging, and they are shaping the future of supply chain finance. Now we can hear a lot about blockchain-powered smart contracts revolutionising trust and transparency all the way to AI-driven predictive analytics optimising inventory management. All of these tools at our disposal are enabling businesses to unlock new levels of efficiency, agility, and resilience.
This process has started way back in the past and it is somehow inevitable. What’s more, it brings constant growth in this segment and this growth is not anywhere near close to stopping. But in order to get a grasp of how innovations and new trends impact the growth, we need to start looking at the numbers and the market outlook in previous years but also estimations for the years to come.
What is the supply chain finance outlook for 2023?
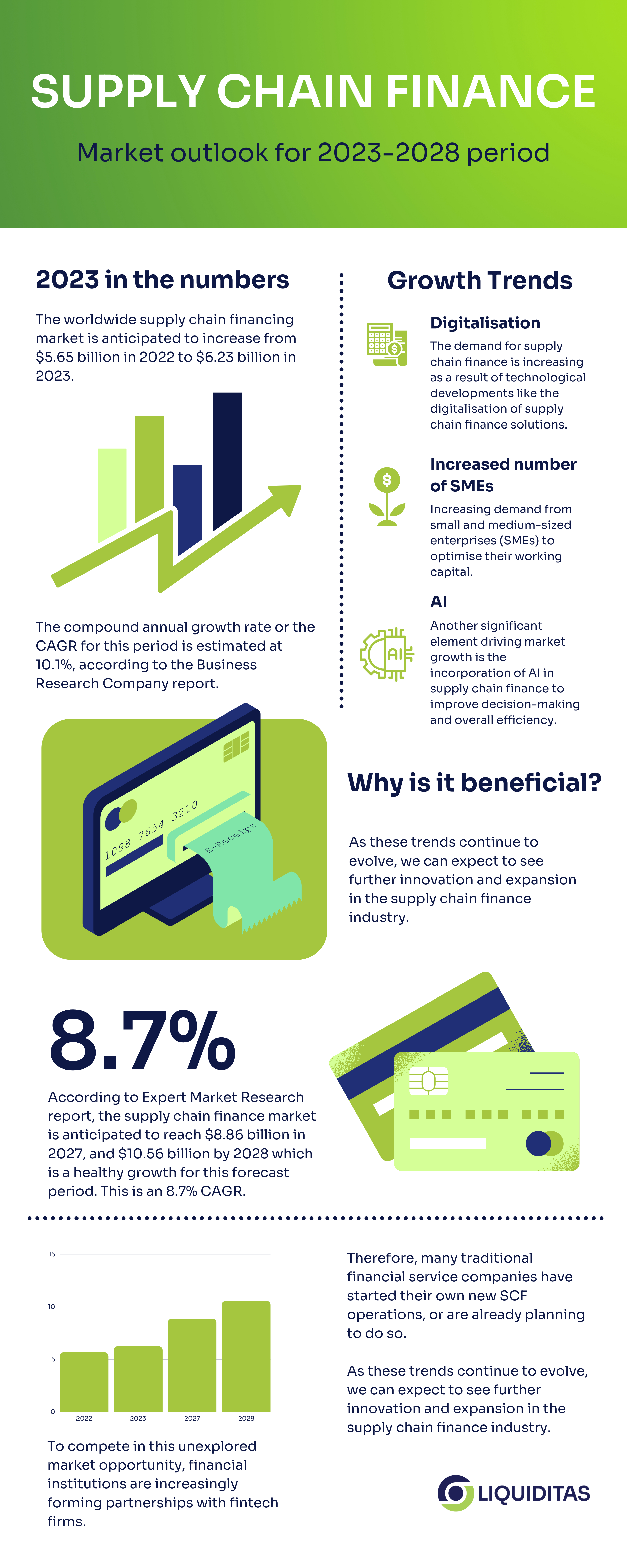
With a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 10.1%, the worldwide supply chain financing market is anticipated to increase from $5.65 billion in 2022 to $6.23 billion in 2023, according to Business Research Company report.
The confrontation between Russia and Ukraine, at least briefly, limited the likelihood of a COVID-19 pandemic-related global economic recovery.
The war between these two countries has resulted in economic sanctions on a number of countries, an increase in prices for commodities, and disruptions in the supply chain, which have increased the cost of goods and services and had an effect on many global markets.
For the period from 2023 until 2028, the market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 8.7%. The Expert Market Research report states that the supply chain finance market is anticipated to reach $8.86 billion in 2027, and $10.56 billion by 2028 which is a healthy growth for this forecast period.
The market for supply chain finance includes the revenue generated by companies that offer a range of supply chain finance services, including real-time data and analytics, reducing fraud risks, handling disputes, digitizing invoice collections, automating manual processes, generating risk-free returns, discounting invoices, and collateral-free solution management. The value of associated goods sold by the service provider or incorporated into the service providing is included in the market value.
Trends in the global supply chain finance market
As mentioned previously, the global market for supply chain finance has been experiencing significant growth, driven by several key trends.
Three prominent factors contributing to this growth are the increasing demand from small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) to optimize their working capital, the integration of artificial intelligence (AI) with supply chain finance solutions, and digitalisation through numerous technological advancements.
Rising demand from SMEs
Small and medium-sized companies are increasingly in need of supply chain financing due to causes including the establishment of new small businesses that emerge on the market almost on a daily basis. These solutions assist businesses in improving their connections with suppliers, working capital optimisation, and cash flow improvement, enabling efficient operation of the company.
- Working capital optimisation: SMEs often face challenges in managing their cash flow and working capital effectively. Supply chain finance provides them with a means to access early payment for their invoices, allowing them to maintain liquidity and continue operations smoothly.
- Access to affordable financing: Traditional financing options, like bank loans, can be challenging for SMEs to secure, particularly for those without a long track record or substantial assets. Supply chain finance offers an alternative by leveraging the creditworthiness of larger buyers in the supply chain, which enables SME suppliers to obtain financing at lower interest rates.
- Enhanced supplier-buyer relationships: Supply chain finance programs can foster stronger relationships between buyers and their suppliers. By offering early payment options, buyers demonstrate a commitment to supporting their suppliers’ financial health, which can lead to more collaborative and mutually beneficial partnerships.
Integration of artificial intelligence (AI):
Another significant element driving global supply chain finance market growth is the incorporation of artificial intelligence to improve decision-making and overall efficiency. Large amounts of data can be analysed by machine learning algorithms to assess any risk, resulting in more precise and timely financing decisions. Moreover, AI can be used in many different scenarios including:
- Enhanced risk assessment: AI-powered algorithms are increasingly being utilised to assess the creditworthiness of suppliers. These algorithms can analyse a wide range of data points, including financial statements, payment histories, and market trends, to provide more accurate risk assessments. This allows financial institutions and supply chain finance platforms to make more informed lending decisions.
- Dynamic discounting and early payment optimisation: AI can optimise dynamic discounting programs, allowing buyers to strategically choose which invoices to pay early based on factors like cash flow, supplier relationships, and available discounts. This dynamic approach ensures that working capital is used efficiently.
- Fraud detection and prevention: AI-driven solutions can identify anomalies and suspicious activities in supply chain finance transactions, helping to prevent fraud. By continuously monitoring for unusual patterns, AI can enhance the security and integrity of the supply chain finance ecosystem.
- Predictive analytics for supply chain management: AI can analyse historical data, market trends, and external factors to make accurate predictions about demand, lead times, and potential disruptions in the supply chain. This information is invaluable for planning and risk mitigation.
Digitalisation
The demand for supply chain finance is increasing as a result of technological developments like the digitalisation of supply chain finance solutions. This allows for safe transactions, increased visibility, faster and transparent transactions, and improved efficiency.
What’s next?
The growth of the supply chain finance market is being propelled by the increasing demand from SMEs for working capital optimisation and the integration of artificial intelligence, which is revolutionising risk assessment, early payment optimisation, fraud prevention, and predictive analytics.
What’s more, to compete in this unexplored market opportunity, financial institutions are increasingly forming partnerships with fintech firms. Therefore, many traditional financial service companies have started their own new SCF operations, or are already planning to do so.
As these trends continue to evolve, we can expect to see further innovation and expansion in the global supply chain finance industry.
Infographic: Global supply chain finance in the numbers